Book now
Book now
IVF is an assisted reproduction technique in which fertilisation —the union of the oocyte with the sperm cell— takes place in vitro, in other words, in the laboratory. Its purpose is to facilitate fertilisation and thus generate embryos that are then transferred to the mother’s uterus to achieve pregnancy.
In vitro fertilisation can be performed using two techniques:

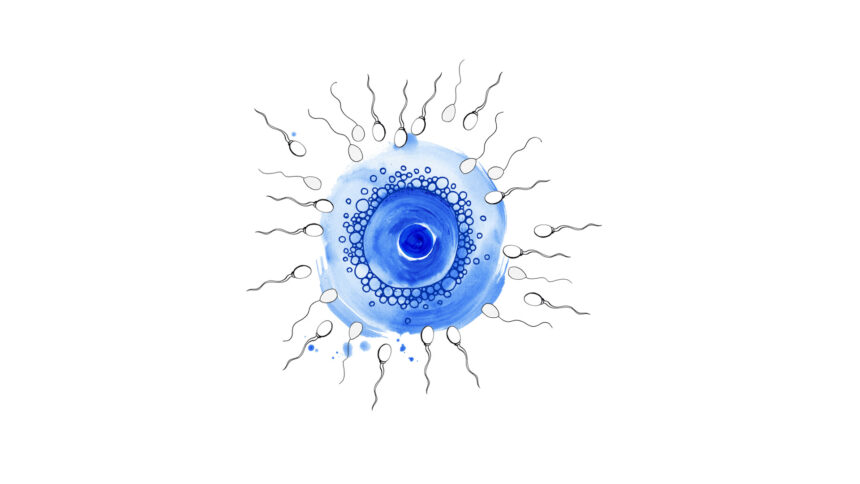
Where the oocytes are put in contact with numerous motile and good quality sperm cells, so that one of them penetrates the egg cell by itself and fertilises it. This process is similar to what happens in the fallopian tubes when pregnancy occurs naturally.

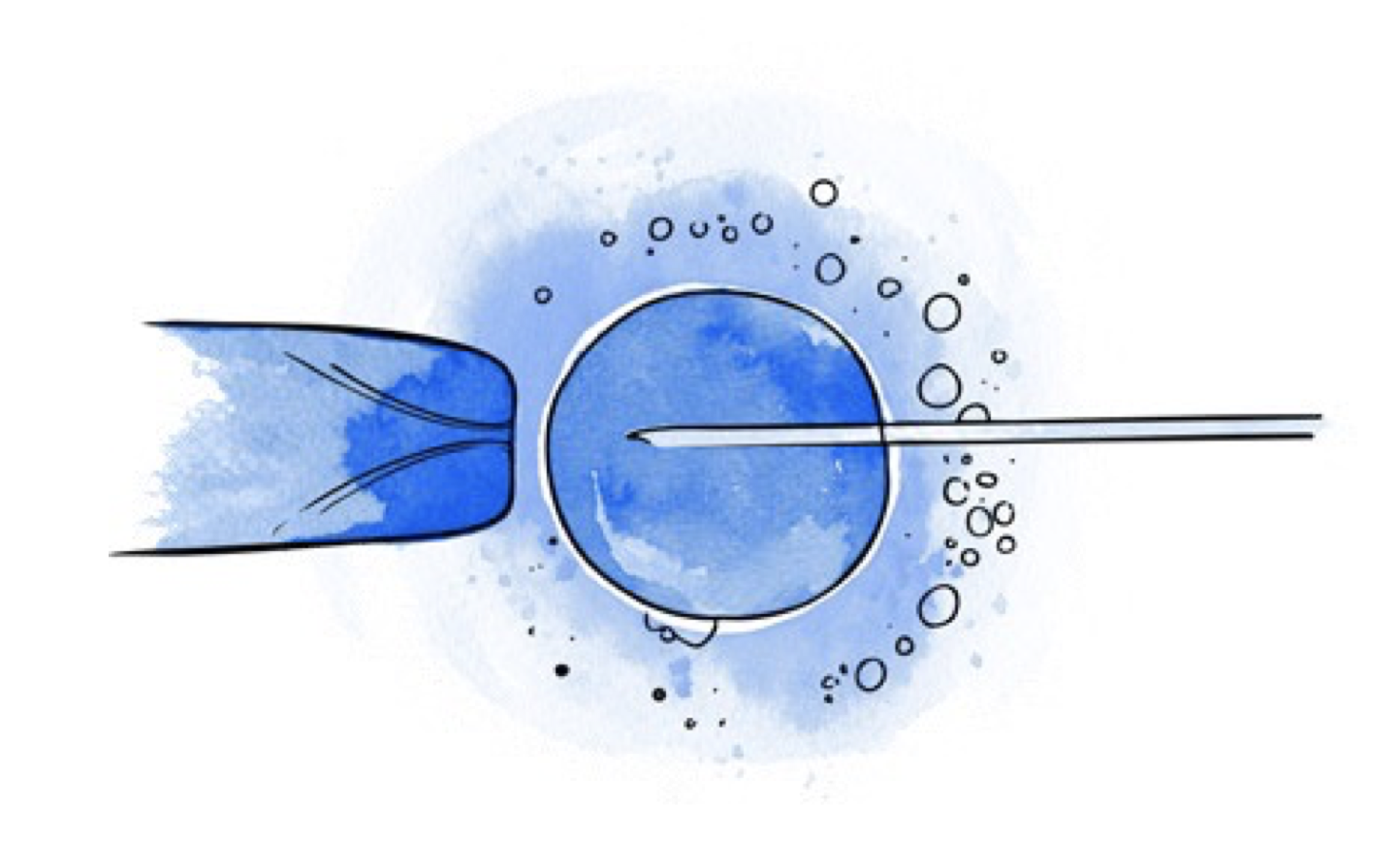
Where a sperm cell is selected and injected into the oocyte with the help of a micromanipulation system. This technique facilitates fertilisation when there are few sperm cells available or when sperm motility is not good.
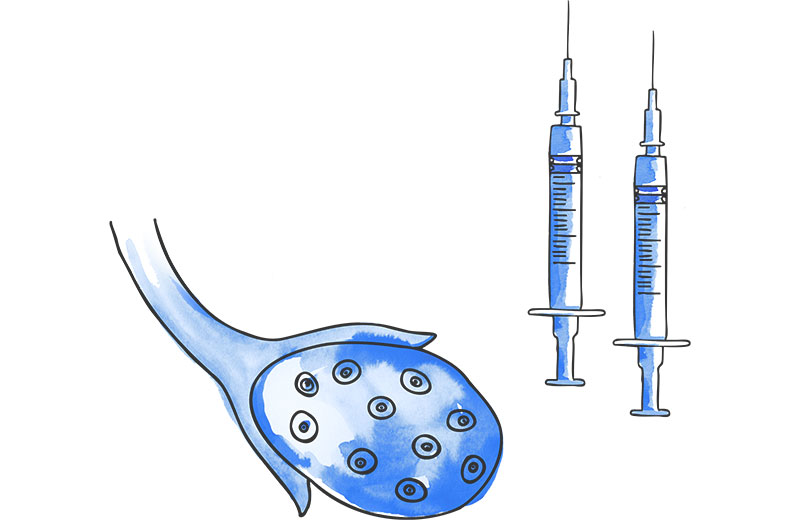

This consists of the administration of injectable hormones to achieve the development of several mature oocytes in the same cycle. The greater the number of oocytes, the greater the probability of obtaining embryos and achieving pregnancy.
The oocytes develop in the ovary, inside small sacs of fluid called follicles. The duration of the stimulation process is usually between 8 and 12 days, during which time ultrasound checks will be performed in order to schedule the extraction at the right time.

Oocyte retrieval is performed by transvaginal puncture performed under ultrasound guidance. This procedure normally takes about 15-30 minutes and is carried out under sedation. The patient will be able to leave after 2 hours rest.
The fluid extracted from the follicles is analysed in the laboratory to collect the oocytes and classify them in accordance with their maturity.

Depending on the technique to be used, IVF or ICSI, the oocytes obtained are prepared for insemination. Simultaneously, the sperm is processed in the laboratory to improve and increase its fertilising capacity.
To perform conventional in vitro fertilisation (IVF), the eggs or oocytes are kept with their surrounding cells (granulosa cells), which allow the sperm cell to interact with the egg in order to fertilise it. These eggs are placed in a dish and left in contact with the sperm cells.
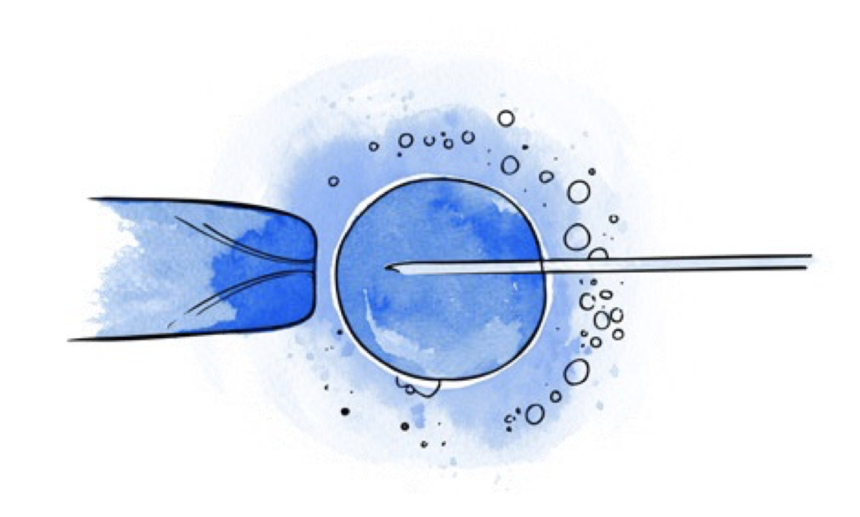
In the case of ICSI, the cells surrounding the egg are removed to identify those that have reached a suitable stage for microinjection (mature oocytes). Subsequently, a single sperm is microinjected into each egg.
From this stage onwards, the oocytes are kept in special incubators that maintain the appropriate conditions for embryonic development. The following day, they are analysed to identify those that have fertilised correctly. The embryos can remain in culture for 2 to 6 days. Depending on each case, they will be transferred to the uterus or cryopreserved for transfer in a later cycle.
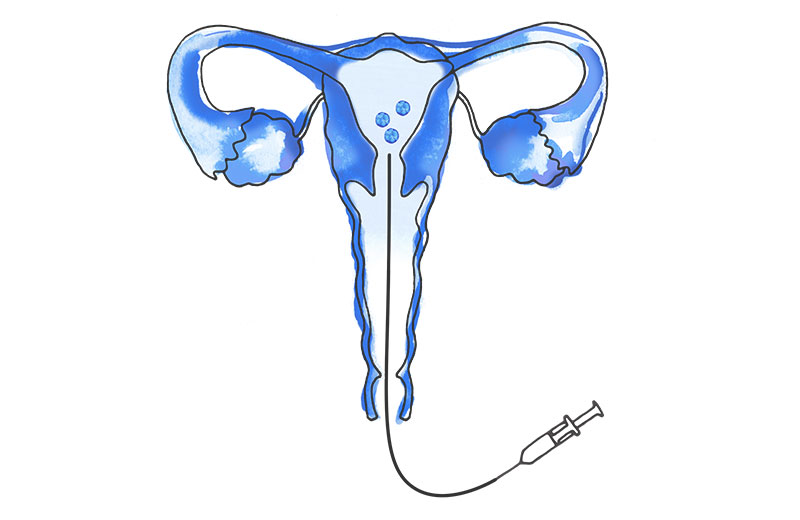

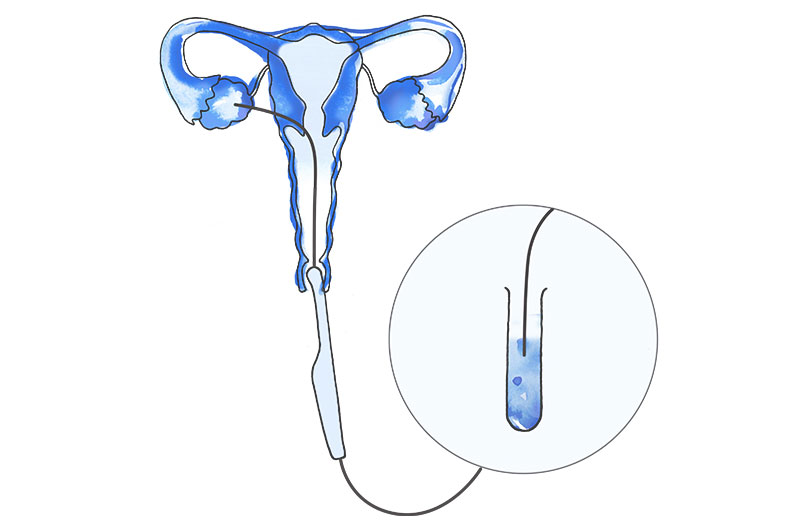
Embryo transfer consists of placing the embryos into the mother's uterus with a very fine cannula, so that implantation (nesting of the embryo in the inner wall or endometrium) can then occur. It is a painless procedure performed vaginally and does not require anaesthesia.

Two weeks after the transfer, a pregnancy test is performed. If the result is positive, your doctor will continue to monitor you until a heartbeat is detected in the embryo, after which you will be referred to your obstetrician.
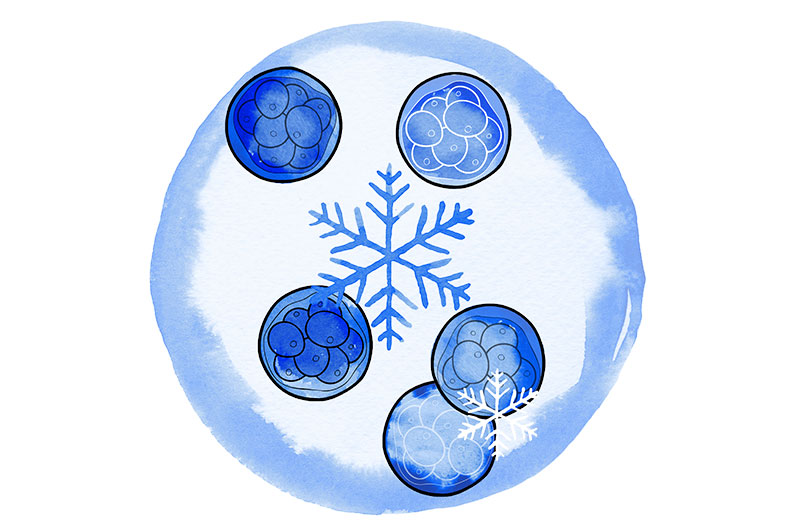


Normally only one embryo is transferred into the uterus, or a maximum of two. All good quality embryos that are not transferred will be cryopreserved.
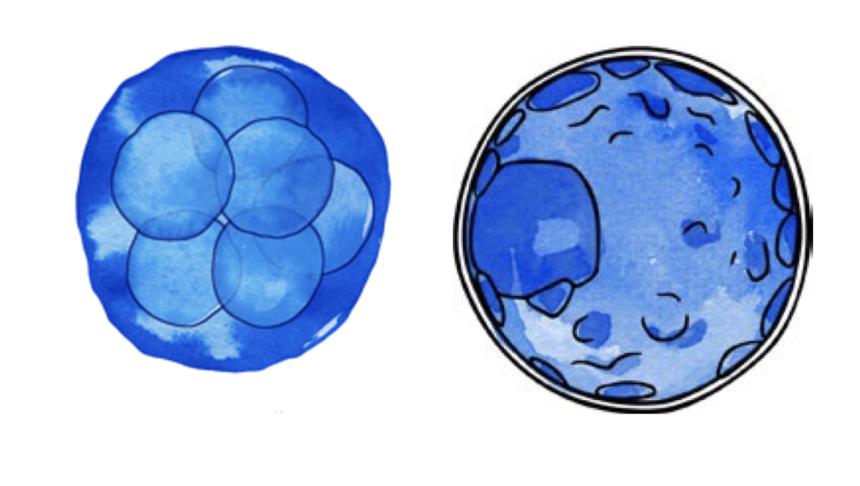
Cryopreservation, or embryo freezing, consists of preserving the embryos at very low temperatures immersed in liquid nitrogen. This process allows them to maintain viability until they are thawed and used in a subsequent cycle.